ce编程软件全称
Title: Understanding CE Programming for 4Axis Control
Introduction
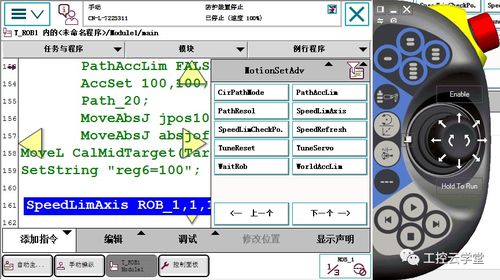
CE programming for 4axis control refers to the implementation of control algorithms and logic in the context of controlling a system with four degrees of freedom. This could apply to various systems, such as robotic arms, CNC machines, or any other mechanical system with four axes of motion. In this discussion, we'll explore the key concepts, techniques, and considerations involved in CE programming for 4axis control.
1. Understanding 4Axis Control Systems
Before delving into CE programming, it's essential to understand the nature of 4axis control systems:
Degrees of Freedom (DOF)
: A system with four axes typically allows movement in four independent directions. Each axis represents a degree of freedom, which can be controlled individually or in combination with others.
Types of Axes
: The axes in a 4axis system can vary depending on the application. Common types include linear (X, Y, Z) and rotational (e.g., Roll, Pitch, Yaw).
Coordinate Systems
: Establishing a consistent coordinate system is crucial for accurate control. This system defines the reference frame for each axis and determines how movements are interpreted.2. Control Engineering (CE) Basics
CE involves designing control systems to achieve desired behaviors or performance. Here are some fundamental concepts relevant to CE programming for 4axis control:
Feedback Control
: Feedback loops are integral to control systems, providing information about the system's current state and allowing adjustments to achieve desired outcomes. Common feedback control techniques include PID (ProportionalIntegralDerivative) control.
Motion Planning
: CE programming often involves planning the trajectory of motion for each axis to accomplish specific tasks efficiently and accurately. This may involve algorithms such as spline interpolation or inverse kinematics.
Sensor Integration
: Sensors play a vital role in providing feedback about the system's state, including position, velocity, and acceleration. Integrating sensors effectively into the control system enhances accuracy and reliability.3. Challenges and Considerations
CE programming for 4axis control presents several challenges and considerations:
Dimensional Complexity
: Managing four axes introduces complexity in terms of coordination, synchronization, and error handling. CE algorithms must account for these factors to ensure smooth operation.
Nonlinear Dynamics
: Mechanical systems often exhibit nonlinear behavior, especially at extreme positions or under varying loads. CE programming may involve nonlinear control techniques to address these dynamics effectively.
Safety and Redundancy
: In applications where precision and safety are critical, CE programming should incorporate redundancy and faulttolerance mechanisms to prevent accidents and minimize downtime.4. Implementation Strategies
When implementing CE programming for 4axis control, several strategies can enhance effectiveness and performance:
Modular Design
: Breaking down the control logic into modular components simplifies development, testing, and maintenance.
Simulation and Testing
: Before deployment, thoroughly simulate and test the control algorithms using software or hardwareintheloop simulations to validate performance and identify potential issues.
Continuous Optimization
: Monitor system performance in realtime and implement continuous optimization techniques to adapt to changing conditions and improve efficiency.5. Case Study: CNC Machining
As a practical example, consider the application of CE programming in CNC machining, where a 4axis system controls the movement of a cutting tool:
Motion Planning
: CE algorithms determine the optimal tool path to fabricate a given component, considering factors such as material properties, tool constraints, and desired surface finish.
Feedback Control
: Sensors provide realtime feedback on tool position, allowing the control system to adjust spindle speed, feed rate, and cutting parameters to maintain accuracy and quality.
Error Compensation
: CE programming may incorporate error compensation techniques to account for machine inaccuracies, tool wear, and environmental factors, ensuring consistent and precise machining results.Conclusion
CE programming for 4axis control involves designing sophisticated algorithms and logic to achieve precise, efficient, and reliable control of complex mechanical systems. By understanding the principles, challenges, and implementation strategies outlined above, engineers can develop robust control systems for various applications, from robotic manipulation to CNC machining.
本文 新鼎系統网 原创,转载保留链接!网址:https://acs-product.com/post/7162.html
免责声明:本网站部分内容由用户自行上传,若侵犯了您的权益,请联系我们处理,谢谢!联系QQ:2760375052 版权所有:新鼎系統网沪ICP备2023024866号-15