设备编程软件
Title: Mastering HTTP Requests in Programming
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is the foundation of data communication on the World Wide Web. It serves as a protocol for communication between client and server. Understanding how to work with HTTP requests in programming is essential for building robust web applications and APIs. Let's delve into the fundamentals and best practices of HTTP request programming.
Overview of HTTP Requests
HTTP requests are messages sent by a client to initiate an action on the server. There are several types of HTTP requests, each serving a different purpose:
1.
GET
: Requests data from a specified resource.2.
POST
: Submits data to be processed to a specified resource.3.
PUT
: Updates a specified resource.4.
DELETE
: Deletes the specified resource.5.
HEAD
: Similar to GET but retrieves only the headers and not the body of the response.6.
PATCH
: Applies partial modifications to a resource.7.
OPTIONS
: Describes the communication options for the target resource.Implementing HTTP Requests in Programming
1. Using Libraries/Frameworks:
a. Python Requests Library:
```python
import requests
GET Request
response = requests.get('https://api.example.com/data')
POST Request
data = {'key': 'value'}
response = requests.post('https://api.example.com/post', data=data)
Handling Response
print(response.status_code)
print(response.json())
```
b. JavaScript Fetch API:
```javascript
// GET Request
fetch('https://api.example.com/data')
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));
// POST Request
fetch('https://api.example.com/post', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify({key: 'value'}),
headers: {'ContentType': 'application/json'}
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => console.log(data))
.catch(error => console.error('Error:', error));
```
2. Manual HTTP Requests:
a. Using cURL (Command Line):
```bash
GET Request
curl https://api.example.com/data
POST Request
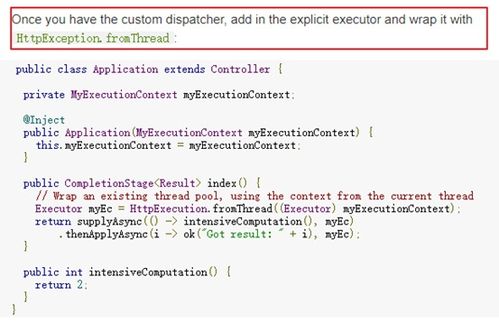
curl X POST d "key=value" https://api.example.com/post
```
b. Using Telnet (Manual TCP Connection):
```bash
telnet api.example.com 80
POST /post HTTP/1.1
Host: api.example.com
ContentType: application/xwwwformurlencoded
ContentLength: 9
key=value
```
Best Practices for HTTP Requests
1.
Use HTTPS
: Always prefer HTTPS over HTTP for secure communication.2.
Handle Errors
: Implement error handling to deal with network issues, timeouts, and server errors.3.
Authentication
: Secure your requests with appropriate authentication mechanisms like API keys, OAuth tokens, or JWT.4.
Parameter Encoding
: Encode request parameters properly to avoid injection attacks and ensure compatibility.5.
Response Validation
: Validate and sanitize responses to prevent security vulnerabilities like XSS and SQL injection.6.
Rate Limiting
: Respect rate limits imposed by APIs to avoid being blocked or throttled.7.
Optimized Payload
: Minimize payload size by using compression techniques like gzip and by removing unnecessary data.8.
Caching
: Utilize caching mechanisms like ETags and cachecontrol headers to reduce server load and improve performance.9.
KeepAlive
: Enable HTTP keepalive to maintain persistent connections and reduce latency.10.
Logging and Monitoring
: Log HTTP requests and responses for debugging and monitor performance metrics for optimization.Mastering HTTP requests in programming empowers developers to create efficient and secure web applications. By understanding the basics, implementing best practices, and utilizing appropriate tools, programmers can build robust systems that communicate effectively over the web. Whether it's fetching data from an API, submitting form data, or updating resources, HTTP requests form the backbone of modern web development.
本文 新鼎系統网 原创,转载保留链接!网址:https://acs-product.com/post/23459.html
免责声明:本网站部分内容由用户自行上传,若侵犯了您的权益,请联系我们处理,谢谢!联系QQ:2760375052 版权所有:新鼎系統网沪ICP备2023024866号-15