生物翻译英文怎么说
Understanding Translation in Biology
In the realm of biology, "translation" refers to a fundamental process that occurs within cells, playing a pivotal role in protein synthesis. Let's delve into the intricate mechanisms and significance of translation in the context of biology.
Overview:
Translation is the process by which ribosomes decode mRNA (messenger RNA) sequences to produce specific proteins. This process occurs in the cytoplasm of cells and involves a complex interplay of various molecules and factors.
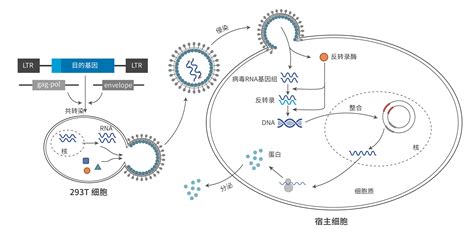
Key Players:
1.
Messenger RNA (mRNA):
mRNA carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes, serving as a template for protein synthesis.2.
Ribosomes:
These molecular machines are responsible for reading the mRNA and assembling amino acids into a polypeptide chain, which forms the protein.3.
Transfer RNA (tRNA):
tRNA molecules ferry amino acids to the ribosome, where they are matched with the appropriate codons on the mRNA during protein synthesis.Process:
1.
Initiation:
The process begins with the binding of the small ribosomal subunit to the mRNA molecule. The ribosome then scans the mRNA until it reaches the start codon (usually AUG), marking the beginning of translation.2.
Elongation:
During this phase, amino acids are added one by one to the growing polypeptide chain. Each amino acid is brought to the ribosome by a specific tRNA molecule, which recognizes the codon on the mRNA through base pairing.3.
Termination:
Translation continues until a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) is encountered on the mRNA. These stop codons signal the ribosome to release the completed polypeptide chain, which then folds into its functional protein structure.Significance:
Translation is a crucial process in biology for several reasons:
Protein Synthesis:
It is the primary mechanism by which cells produce proteins, which are essential for virtually all cellular functions and processes.
Gene Expression:
Translation plays a key role in regulating gene expression, as the rate of protein synthesis can be controlled in response to various internal and external signals.
Diversity and Specificity:
The specific sequence of nucleotides in mRNA determines the sequence of amino acids in the resulting protein, allowing for the vast diversity and specificity of proteins found in living organisms.Future Directions:
Advancements in molecular biology and biotechnology continue to deepen our understanding of translation and its significance. Research efforts are focused on unraveling the complexities of translation regulation, developing novel therapeutics targeting translationrelated processes, and engineering proteins with desired properties for various applications.
In conclusion, translation is a fundamental process in biology that drives protein synthesis, gene expression, and cellular function. Understanding the intricacies of translation is essential for unraveling the complexities of living organisms and holds promise for future discoveries and innovations in biomedicine and beyond.
Now that we've explored the essence of translation in biology, it's evident that this process is not just a molecular dance within cells but a cornerstone of life itself.
本文 新鼎系統网 原创,转载保留链接!网址:https://acs-product.com/post/18210.html
免责声明:本网站部分内容由用户自行上传,若侵犯了您的权益,请联系我们处理,谢谢!联系QQ:2760375052 版权所有:新鼎系統网沪ICP备2023024866号-15








