vb.netfunction
Title: Exploring Essential Functions in VB.NET Programming
In VB.NET programming, functions play a crucial role in organizing and executing code efficiently. Let's delve into some fundamental aspects of functions in VB.NET, including their syntax, usage, and best practices.
1. Syntax of a Function in VB.NET:
In VB.NET, a function is defined using the `Function` keyword followed by the function name and parameters (if any). Here's a basic syntax:
```vbnet
Function functionName(ByVal param1 As DataType, ByVal param2 As DataType) As ReturnType
' Function body
' Return statement
End Function
```
`functionName`: Name of the function.
`param1`, `param2`, etc.: Parameters passed to the function.
`DataType`: Data type of parameters and return type.
`ReturnType`: Data type of the value returned by the function.
2. Usage of Functions:
Functions are used to encapsulate a block of code that performs a specific task and can return a value to the calling code. Here's how you can use functions in VB.NET:
Example 1: Simple Addition Function
```vbnet
Function Add(ByVal num1 As Integer, ByVal num2 As Integer) As Integer
Return num1 num2
End Function
```
Example 2: Function Call
```vbnet
Dim result As Integer
result = Add(5, 3)
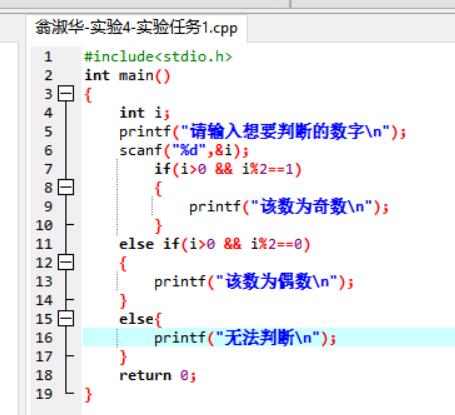
Console.WriteLine("Result: " & result) ' Output: Result: 8
```
3. Passing Parameters:
Parameters can be passed to functions by value or by reference:
By Value:
Changes made to the parameter inside the function do not affect the original value outside the function.
By Reference:
Changes made to the parameter inside the function affect the original value outside the function.Example 3: Passing Parameters
```vbnet
Sub Update(ByVal value As Integer)
value = value 1
End Sub
Dim num As Integer = 5
Update(num)
Console.WriteLine("Value: " & num) ' Output: Value: 5
```
4. Return Statement:
The `Return` statement is used to exit a function and optionally return a value to the calling code.
Example 4: Return Statement
```vbnet
Function GetSquare(ByVal num As Integer) As Integer
Return num * num
End Function
```
5. Best Practices:
To write efficient and maintainable code, consider the following best practices:
Descriptive Names:
Use descriptive names for functions to indicate their purpose.
Single Responsibility:
Each function should have a single responsibility.
Error Handling:
Implement error handling within functions to handle unexpected situations gracefully.
Comments:
Add comments to explain complex logic or algorithm used in the function.Conclusion:
Functions are essential building blocks in VB.NET programming, allowing you to encapsulate logic, promote reusability, and enhance code readability. By understanding the syntax and best practices, you can leverage functions effectively in your VB.NET projects.
本文 新鼎系統网 原创,转载保留链接!网址:https://acs-product.com/post/12733.html
免责声明:本网站部分内容由用户自行上传,若侵犯了您的权益,请联系我们处理,谢谢!联系QQ:2760375052 版权所有:新鼎系統网沪ICP备2023024866号-15