plc编程器工作原理
Title: Introduction to PLC Programming Machines
Overview
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) programming machines play a crucial role in industrial automation, enabling the control of various processes in manufacturing environments. These machines are designed to facilitate the programming, testing, and deployment of PLC systems, which are integral to automating tasks in diverse industries such as automotive, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and more.
Understanding PLC Programming Machines
PLC programming machines, also known as PLC programming tools or PLC development environments, are specialized hardware and software systems tailored for PLC programming tasks. They provide engineers and technicians with a platform to create, modify, and debug PLC programs efficiently. Here's a breakdown of the key components and functionalities typically found in PLC programming machines:
1.
Hardware Components:
Industrial PC (IPC):
Often the backbone of PLC programming machines, industrialgrade PCs provide the processing power and interface capabilities required for PLC programming tasks. These PCs are ruggedized to withstand harsh industrial environments.
Input/Output (I/O) Modules:
Some PLC programming machines may include I/O modules for simulating or connecting to physical devices, allowing developers to test PLC programs in a simulated or realworld environment.
Communication Interfaces:
Interfaces such as Ethernet, USB, serial ports, and fieldbus connections enable communication between the PLC programming machine and PLCs or other devices.2.
Software Environment:
Programming Software:
PLC programming machines come equipped with software suites tailored for PLC development, such as ladder logic editors, function block diagram editors, structured text editors, and mnemonic editors. These tools enable developers to write PLC programs using various programming languages supported by PLCs.
Simulation Tools:
Many PLC programming machines offer simulation capabilities, allowing developers to test PLC programs without the need for physical hardware. Simulation tools simulate the behavior of PLCs and connected devices, facilitating thorough testing and debugging.
Diagnostic Tools:
Diagnostic features help developers identify and troubleshoot issues in PLC programs. These tools may include online/offline debugging, realtime monitoring, and error log analysis functionalities.
Integration Tools:
Some PLC programming machines support integration with other software systems such as SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) and MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems), enabling seamless data exchange and coordination between different layers of industrial automation systems.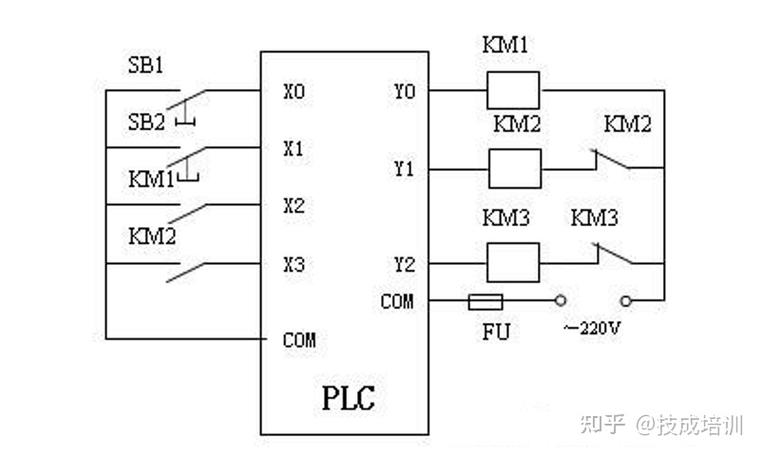
Benefits of PLC Programming Machines
1.
Efficiency:
PLC programming machines streamline the development process by providing intuitive interfaces, powerful programming tools, and efficient debugging capabilities, reducing development time and effort.2.
Flexibility:
These machines support various PLC programming languages and are compatible with a wide range of PLC hardware, offering flexibility to developers in choosing the most suitable programming approach for their applications.3.
Reliability:
Industrialgrade hardware and software components ensure the reliability and robustness of PLC programming machines, suitable for deployment in demanding industrial environments.4.
Scalability:
PLC programming machines can scale to accommodate projects of different sizes and complexities, from smallscale applications to largescale industrial automation systems.5.
CostEffectiveness:
While initial investments may be significant, PLC programming machines help minimize costs in the long run by accelerating development cycles, reducing downtime, and optimizing system performance.Considerations for Selecting PLC Programming Machines
When choosing a PLC programming machine, consider the following factors:
1.
Compatibility:
Ensure compatibility with the PLC hardware and software platforms used in your applications.2.
Ease of Use:
Look for intuitive interfaces and comprehensive documentation to facilitate the learning curve for developers.3.
Support and Maintenance:
Consider the availability of technical support, software updates, and maintenance services to ensure smooth operation and timely resolution of issues.4.
Scalability and Expandability:
Evaluate the scalability and expandability options of the PLC programming machine to accommodate future growth and evolving project requirements.5.
Integration Capabilities:
Assess integration capabilities with other automation systems and enterpriselevel software solutions for seamless data exchange and interoperability.Conclusion
PLC programming machines are indispensable tools for developing and deploying PLCbased automation solutions across various industries. By providing a robust hardware and software environment tailored for PLC programming tasks, these machines empower engineers and technicians to create efficient, reliable, and scalable automation systems. When selecting a PLC programming machine, consider factors such as compatibility, ease of use, support, scalability, and integration capabilities to maximize the benefits and ensure the success of your automation projects.
本文 新鼎系統网 原创,转载保留链接!网址:https://acs-product.com/post/11483.html
免责声明:本网站部分内容由用户自行上传,若侵犯了您的权益,请联系我们处理,谢谢!联系QQ:2760375052 版权所有:新鼎系統网沪ICP备2023024866号-15